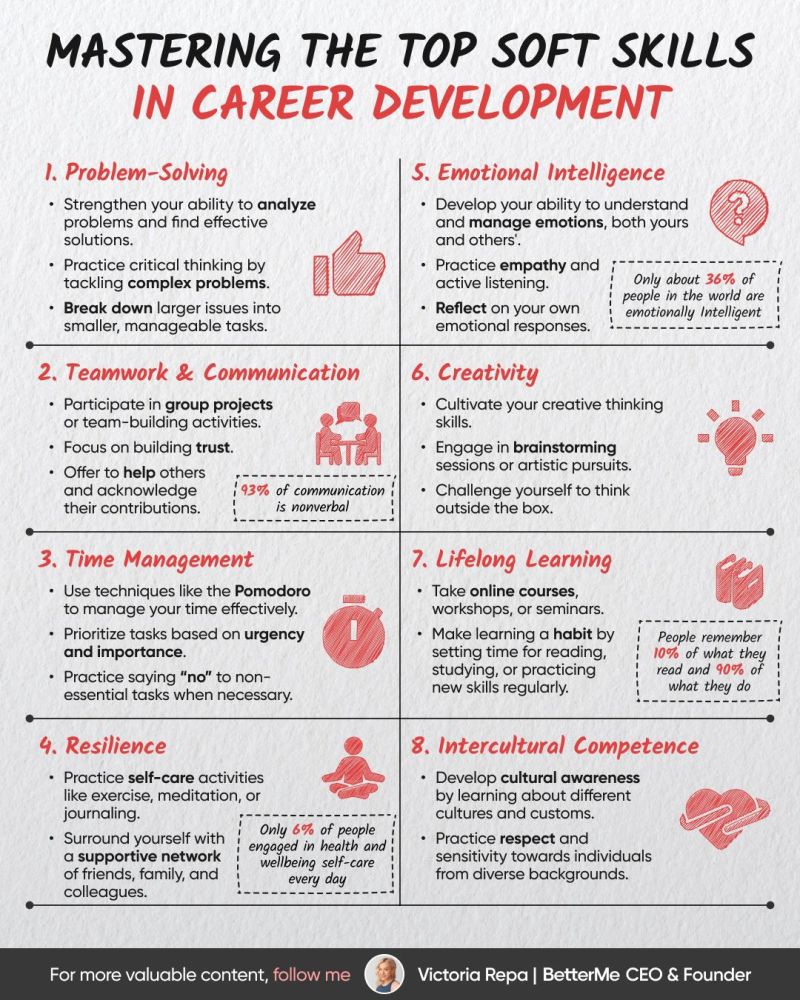
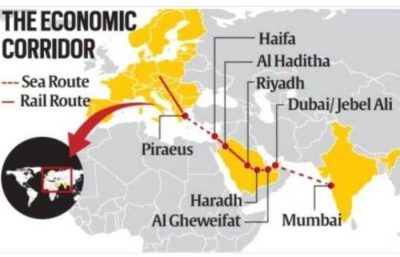
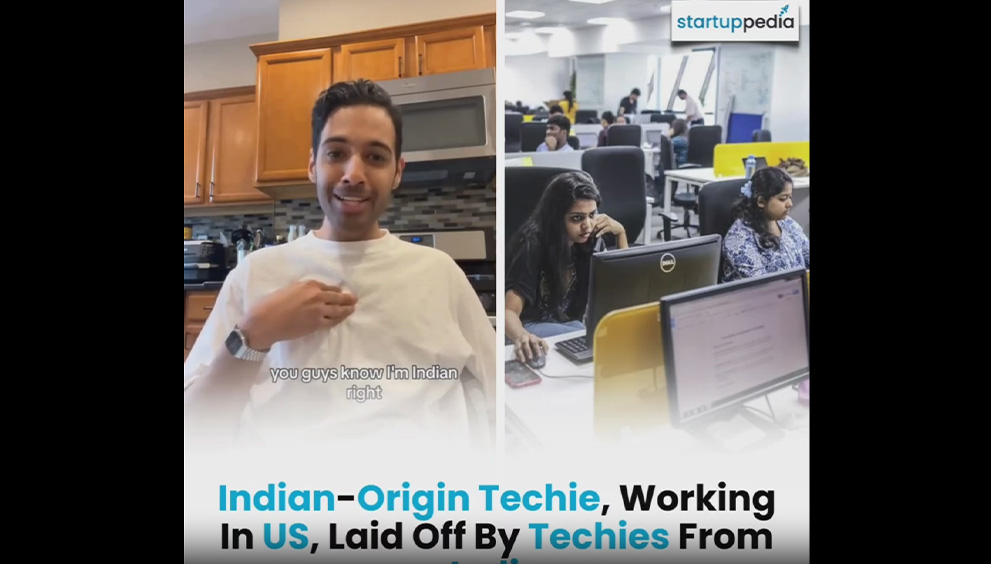
By Harshvardhan Sharma
NEW DELHI: The Data Protection Board of India, as established by the newly enacted Digital
Personal Data Protection Act 2023, represents a significant evolution in India’s approach to data
privacy and security. This article aims to distill the essence of the Board’s creation, its structure,
functions, and the expected impact on the digital landscape of India, based on the details
provided in the legal draft of the Act.
Establishing the Data Protection Board
The Data Protection Board of India will play a key role in enforcing data protection laws in the
country. As a corporate entity, it has the legal status and authority to own property, enter into
contracts and engage in litigation if required. The Board’s headquarters will be situated in a
location designated by the Central Government, emphasizing its national importance and
centralized approach to data protection.
Also Read – What Are The Rights And Duties Of Data Principal Under DPDP Act 2023
Composition and Oversight
The Board will consist of a Chairperson and a specific number of members designated by the
Central Government. These members will be selected based on their expertise in various relevant
fields such as data governance, law, digital economy, and information technology, among others.
The board’s multi-disciplinary composition ensures a comprehensive approach to data protection,
combining legal, technical, and administrative perspectives.
Functions and Powers of Data Protection
Board
The Board has been bestowed with comprehensive authority to manage immediate corrective
actions in case of a data breach, investigate grievances related to personal data breaches, and
levy fines for violations of the Act. Moreover, the Board is responsible for supervising the
adherence of Data Fiduciaries and Consent Managers to their responsibilities, highlighting the
Board’s pivotal position in safeguarding the rights of data principals.
Operational Framework
The Board has a unique operational framework that focuses on digital functionality, with the goal
of functioning as a “digital office”. This approach is in line with the digital nature of the data it aims
to protect and ensures efficiency in handling complaints, inquiries, and decision-making
processes.
Also Read – Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 Navigating India’s Data Privacy
Revolution [Read DPDP Act]
Independence and Accountability
The Board is created to operate as a self-sufficient group, which is a critical aspect that supports
its believability and efficiency. Its self-sufficiency is important to guarantee impartial supervision
of data protection practices throughout both the public and private sectors. Additionally, the rule
that ex-members cannot immediately join any entity they formerly oversaw strengthens the
honesty and impartiality of the Board.
Implications for India’s Digital Future
The Data Protection Board of India is a crucial step towards safeguarding personal data, boosting
consumer confidence in digital services, and promoting innovation in the digital economy. Its
success will depend on the effective execution of its mandate and its ability to adapt to the rapidly
evolving digital world. As it begins its operations, all eyes will be on how it shapes the practices of
data protection in India, setting precedents for others to follow in the pursuit of a secure and
trustworthy digital environment.