In the contemporary landscape of cyber and forensics security, the expertise of Indian military veterans presents an invaluable asset. The National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) backed by the National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme (NFIES) are geared towards meeting India’s expanding forensic needs and improving the criminal justice system. Central to this strategy are the establishment of new campuses, the creation of Central Forensic Science Laboratories (CFSLs), and the enhancement of infrastructure at NFSU and other campuses. By integrating military veterans into these initiatives, NFIES can leverage their unique skill sets to solve cases more effectively and efficiently.
Strategic Importance of NFIES
The scheme underscores India’s commitment to fortifying its criminal justice system with robust forensic capabilities. It addresses the pressing need for trained forensic professionals to expedite and enhance the scientific examination of evidence, critical for efficient law enforcement and judicial processes. This initiative aligns with the government’s objective of achieving a conviction rate exceeding 90% by mitigating case backlogs and ensuring timely forensic analyses, crucial under new criminal laws mandating forensic investigations for serious offenses. India unable to fill 30% of cyber security jobs due to skill gap. Although India had 40,000 job openings for cyber security professionals by 2023, 30% of these vacancies could not be filled due to huge skill shortage, as estimated by Team Lease Digital.

NFSU Builds Bridges between forensic science and India’s justice delivery systems
NFSU aims to meet India’s expanding need for forensics in criminal investigations and improve the criminal justice delivery system. To keep pace with the advancements in academics and technology, the university has planned academic collaboration across the world in a big way which stands today with 186 multi-disciplined institutions.
As a super-specialized institution, NFSU has taken it upon itself to lead from the front in imparting high-quality technical education, undertaking high-end scientific research, and developing high-skilled experts in varied areas of Forensic Sciences and allied subjects. NFSU encourages Indian Military Veterans to actively participate in this national mission considering their suitability and availability in critical capacity building of necessary skills and roles.
How NFSU and Veterans Can Close The Skill Gap
Establishment of National Forensic Sciences University Campuses: The expansion of educational facilities for forensic sciences across the country is a critical component of NFIES. Veterans, with their extensive training and discipline, can contribute significantly as educators and trainers. Their experience in high-stress environments and methodical approach to problem solving make them ideal candidates for teaching future forensic experts.
Creation of Central Forensic Science Laboratories (CFSLs): Setting up new CFSLs nationwide aims to enhance forensic examination capacities. Veterans’ backgrounds in investigation, surveillance and intelligence align perfectly with the needs of these laboratories. Their ability to meticulously analyze evidence and manage complex cases can lead to more accurate and timely forensic analyses, thus aiding the judicial process.
Enhancement Campus Infrastructure: Upgrading the infrastructure at the Delhi campus will further solidify NFSU’s role in forensic science education and research. Veterans can play a pivotal role in this enhancement by bringing their academic, administrative, project management and logistical expertise to ensure that the facility meets the highest standards of operational efficiency and security.
The Unique Qualities Veterans Bring to Cyber Security and Forensic Science
Investigation and Surveillance: Veterans are trained to conduct thorough investigations and maintain rigorous surveillance. These skills are directly transferable to forensic science, where attention to detail and comprehensive analysis are crucial. Their ability to follow leads, gather intelligence and piece together information can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of forensic investigations.
Investigation and Risk Management: With a keen eye for detail and extensive training in risk management, veterans can adeptly identify potential threats and vulnerabilities within cyber and forensic frameworks. Their investigative skills, honed through years of military service, allow them to uncover hidden connections and draw insightful conclusions from seemingly disparate pieces of information.
Business Contingency & Continuity: In the realm of cyber security, veterans’ experience in protecting sensitive information and critical infrastructure is invaluable. They are well versed in implementing stringent security protocols and responding swiftly to security breaches. Their proactive approach to safeguarding data and systems can prevent cyber-attacks and
mitigate their impact on forensic operations.
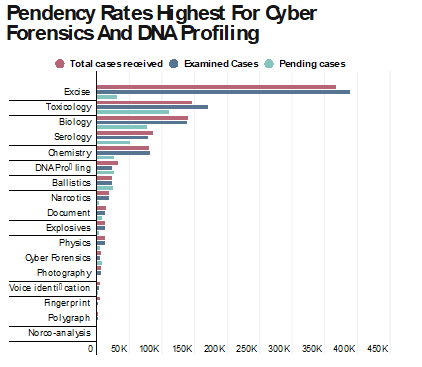
Reduce Legal Cases with Veteran Expertise
Veterans’ skills can lead to the resolution of complex cases more swiftly and accurately. Their methodical approach to investigation ensures that no detail is overlooked, and their experience in high-pressure environments means they can handle the demands of forensic casework with composure and efficiency. By integrating veterans into the NFIES framework, we can enhance the capacity and effectiveness of forensic science in India.
The integration of Indian military veterans into the cyber and forensic security domain, particularly through initiatives like NFIES, offers a dual benefit: it provides a productive career path for veterans while significantly boosting the capabilities of India’s forensic infrastructure. Their unique skill sets in investigation, surveillance, risk management and business continuity make them indispensable assets in solving large numbers of cases and improving the overall efficacy of the criminal justice system.
OSInt. Data & Images from open sources. Excerpts from an article first published on IndiaSpend